Suspensory ligament damage in horses – causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Suspensory ligament damage is one of the most common and serious injuries in horses, especially in competitive sports. This injury can have serious effects on your horse's mobility and quality of life. In this comprehensive article, you will receive all the important information on the subject: from the causes and symptoms to the correct treatment and prevention. With the right knowledge, you can support your horse's health and prevent possible injuries.
What is a suspensory ligament injury?
The suspensory ligament is one of the most important structures in a horse's leg. It begins above the fetlock and extends down to the sesamoid bones and the coronary bone. As the central support of the fetlock joint, it plays a crucial role in the horse's movement and stability. Suspensory ligament damage is an injury to this ligament, which, depending on the severity, can range from a slight inflammation to a complete tear. Such injuries are particularly common in equestrian sports, where the musculoskeletal system is subject to high levels of stress.

How does suspensory ligament damage occur?
There are various causes that can lead to suspensory ligament damage. The most common causes are:
1. Excessive stress
Horses that compete in competitive sports are particularly susceptible to suspensory ligament damage. This is especially true for disciplines such as show jumping, eventing and dressage, where the horse must constantly perform at its best. Repeated jumps or heavily stressed movements place considerable strain on the suspensory ligament.
2. Insufficient warm-up
If a horse is not warmed up sufficiently before intensive training or competition, the risk of injury increases. The muscles, tendons and ligaments are then not sufficiently supplied with blood and stretched, which can lead to overstrain.
3. Soil conditions
Another important factor is the ground conditions on which the horse is trained or exercised. Hard ground increases the impact on the legs, while ground that is too soft (such as deep sand) places greater strain on the musculoskeletal system as the horse has to work its way through the loose ground. Uneven ground can also lead to incorrect loading and thus damage the suspensory ligament.
4. Genetic predisposition and malpositions
Some horse breeds or individually bred lines have a genetic predisposition to weaker tendons and ligaments, which increases the risk of suspensory ligament damage. In addition, misalignments of the limbs lead to uneven loads and thus to overstraining of individual tendons and ligaments.
Symptoms of Suspensory Ligament Damage in Horses
Sustain ligament damage usually manifests itself through symptoms such as lameness. The intensity and type of lameness can vary depending on the severity of the injury. The following symptoms are typical:
-
Lameness : The horse often limps more on soft ground than on hard ground.
-
Swelling and warmth : Visible swelling may occur around the tube of the horse's leg, often accompanied by warmth.
-
Irregular gait : Even the smallest irregularities in the movement pattern can indicate incipient suspensory ligament damage.
It is important to take even the smallest signs of suspensory ligament damage seriously and to consult a veterinarian early on to avoid making the damage worse.
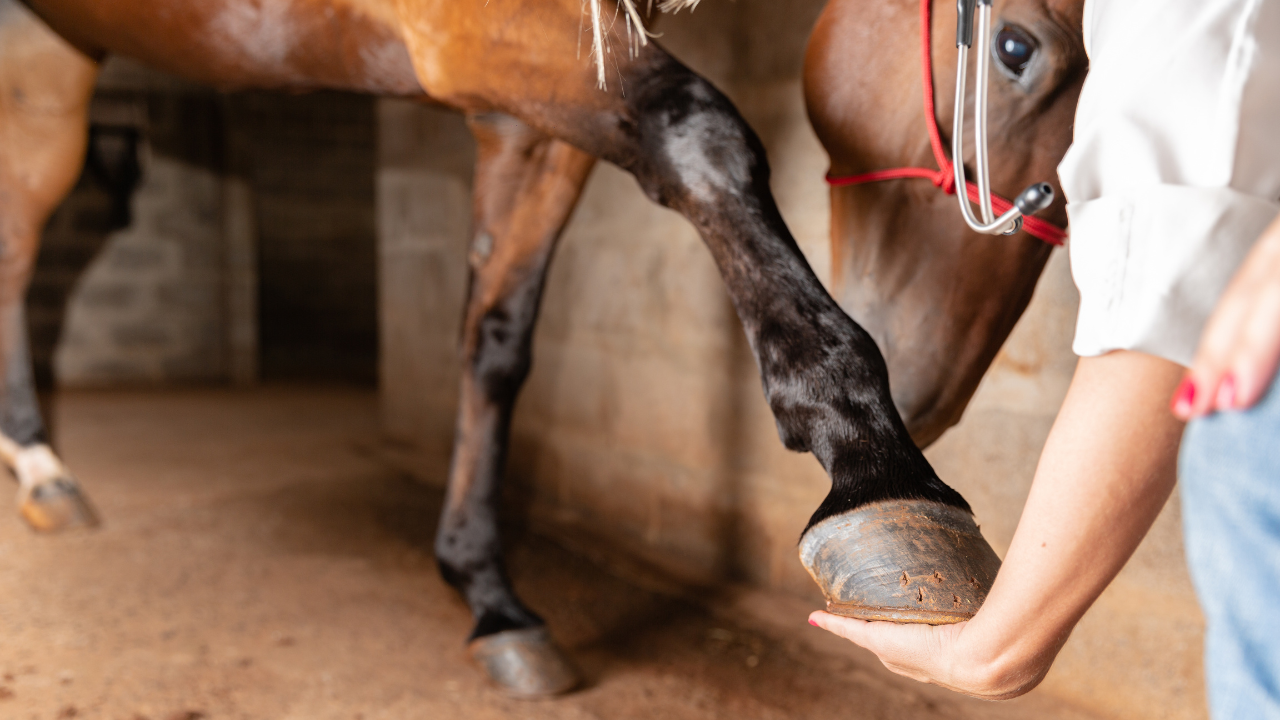
Diagnosis of a suspensory ligament injury in horses
The diagnosis of a suspensory ligament injury is usually made by the veterinarian. First, the horse is shown walking and trotting on different types of ground. The lameness is often more pronounced on soft ground. In addition, the veterinarian carries out a flexion test to test the resilience of the tendons.
If swelling and warmth are present, this is already a clear indication of suspensory ligament damage. For a more precise diagnosis, a Ultrasonic performed to determine the extent of the injury. In severe cases, especially in cases of diffuse or poorly visible damage, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) be necessary.
What types of suspensory ligament damage are there in horses?
A suspensory ligament injury can have different manifestations, which relate to the severity and type of injury:
-
Irritation : A mild form of injury in which the suspensory ligament is minimally affected. A short period of rest is often sufficient.
-
Strain : A greater strain that leads to overstretching of the suspensory ligament. In this case, the horse must be protected for a longer period of time.
-
Inflammation : A reaction to excessive strain in which the suspensory ligament is severely swollen and warmer than the surrounding tissue.
-
Tear of the tendon fibers : In particularly severe cases, individual fibers or even the entire tendon can tear. In such cases, healing is slow and the horse may never be able to bear full weight again.
First measures in case of suspensory ligament damage in horses
As soon as you suspect suspensory ligament damage, you should immediately immobilize the horse and cool the leg. Cold therapy helps to reduce swelling and inflammation. box rest is indispensable in the acute phase to prevent further strain on the injured suspensory ligament.
It is important that you do not treat on your own, but always consult a veterinarian. They can assess the severity of the injury and suggest the appropriate treatment.
Treatment options for suspensory ligament damage in horses
Healing from suspensory ligament damage requires time, patience and precise coordination of treatment. Depending on the severity of the injury, different treatment approaches can be chosen:
-
Cold and heat therapy : In the acute phase, cold helps to reduce swelling. In later phases, heat can promote blood circulation and aid healing.
-
Shock wave therapy : This modern form of therapy stimulates blood circulation and metabolism in the injured tissue and thus accelerates the healing process.
-
Autologous blood therapy : In this method, processed blood plasma is injected into the tendon to promote regeneration and minimize the formation of scar tissue.
-
Physiotherapy and controlled exercise : After a period of absolute rest, the horse should be carefully accustomed to exercise again. Controlled walking is particularly important to make the horse's tendons and tendon fibers supple again and prevent adhesions.
How long does it take to heal from tendon injuries?
The duration of the healing process depends largely on the extent of the injury. In the case of minor irritation, the horse can be put under strain again after just a few weeks, while more serious injuries require several months, sometimes even up to a year, to heal completely. It is important that you closely monitor the healing process in consultation with your veterinarian and do not put strain on the horse again too soon. Putting strain on the horse too soon can delay recovery and increase the risk of permanent damage.
Nutrition as a Support for Recovery
Proper feeding plays an important role in the healing of tendon injuries. Certain nutrients support the regeneration of tendons and ligaments. These include:
-
Magnesium : Promotes muscle and tendon health and helps prevent cramps.
-
Vitamin E : Has an antioxidant effect and protects tendon cells from damage caused by free radicals.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids : have an anti-inflammatory effect and support the healing of tissue damage.
Make sure that the horse does not receive food that is too high in energy during the rest period, as it will have less exercise and may gain weight more quickly.

physiotherapy and rehabilitation
After the acute phase, rehabilitation begins. One of the most important measures is Walking therapy , in which the horse is slowly and carefully brought back into motion. This process must be carried out gradually in order not to overload the freshly healed tissue. Close cooperation with a physiotherapists or chiropractor can help to relieve tension and restore the horse's mobility.
Long-term consequences of suspensory ligament damage
Even after successful recovery from suspensory ligament damage, the affected leg often remains more sensitive than before. Therefore, you should always pay particular attention to signs of overload and not start training your horse intensively again too soon. Some horses tend to have recurring problems after such damage, especially if the cause has not been corrected.
Prevention of suspensory ligament damage
The best treatment for suspensory ligament damage is prevention. You can minimize the risk of suspensory ligament damage by taking the following measures:
-
Regular hoof care : Well-cared for hooves ensure even loading and prevent misalignments that could place unnecessary strain on the suspensory ligament.
-
Gradual warm-up : Start each training session with a slow and controlled warm-up program to prepare the tendons and muscles for the upcoming strain.
-
Avoid deep ground : Riding on ground that is too soft or deep, such as sand, can put a lot of strain on the tendons. Make sure the training ground is well prepared to reduce the strain.
-
Varied training : Varied training plans that do not only focus on intensive jumping or fast gaits can help to avoid overloading the tendons on one side. Also make use of rest periods and gymnastic exercises.
How do you recognize the first signs of impending suspensory ligament damage?
Many horses show small signs before acute lameness that you should take seriously. These include:
-
A slight hesitation when transitioning from walk to trot.
-
Minimal irregularities in gait, often only noticeable on soft ground.
-
A slight swelling in the area of the suspensory ligament, which sometimes disappears after training.
If you notice these signs, you should act immediately. A break in training and a check-up by a veterinarian can prevent the damage from getting worse.
Prognosis: Can my horse be fully loaded again after a suspensory ligament injury?
Whether a horse can fully bear weight again after a suspensory ligament injury depends on the severity of the injury and the correct rehabilitation. Mild to moderate injuries often heal completely if they are detected and treated early. In many cases, horses can return to their original level of performance, especially if the cause of the injury has been eliminated.
However, in cases of severe injuries or complete tearing of the suspensory ligament, the prognosis may be worse. In some cases, horses must be taken out of sport and used as leisure horses to avoid further overload.
Special risks for sport horses: What do you have to consider?
Sport horses are particularly susceptible to suspensory ligament damage, especially in disciplines such as show jumping or dressage. These horses are often exposed to high levels of stress that place a lot of strain on the suspensory ligament. If you have a sport horse, you should pay attention to the following:
-
Breaks in daily training : Horses that train regularly at a high level need sufficient rest periods to regenerate.
-
Regular check-ups : A regular check of the tendon health by the veterinarian can help to detect tendon damage and the first signs of suspensory ligament damage early.
-
Adapted equipment : Particularly well-fitting horseshoes or special fittings can help to provide the horse with optimal support and distribute the load evenly.
Role of the veterinarian in prevention and aftercare
An experienced veterinarian plays a central role in the treatment and prevention of suspensory ligament damage. In addition to diagnosis and choosing the right therapy, the veterinarian also accompanies your horse through the rehabilitation phase. Regular check-ups and ultrasound examinations help to monitor the healing process and make adjustments to training.
The collaboration with a physiotherapists can be useful to maintain the horse's mobility and relieve tension through targeted exercises.
Conclusion: Suspensory ligament damage in horses – patience, prevention and proper care are crucial
Suspensory ligament damage is a complex and serious injury that requires careful and long-term treatment. It is crucial for horse owners to recognize the symptoms early and take immediate action. The correct diagnosis by a veterinarian plays a central role in starting the appropriate treatment. Depending on the severity of the damage, the healing phase can last from several months to a year, during which the horse must be carefully monitored and gradually accustomed to exercise.
One of the most important findings is that prevention is the key to preventing suspensory ligament damage. You can significantly reduce the risk through regular hoof care, a balanced training program and paying attention to suitable ground conditions. Warm-up and cool-down phases should always be observed, especially in competitive sports, where the load on the limbs is high. Genetic factors and possible misalignment of the limbs must also not be ignored, as they can increase the risk of suspensory ligament damage.
Modern therapy methods such as shock wave therapy or autologous blood therapy (PRP) offer good opportunities to accelerate the healing process and support the regeneration of the damaged suspensory ligament. Nevertheless, recovery from suspensory ligament damage remains a lengthy process that requires a lot of patience and close cooperation with veterinarians and therapists.
In summary, it can be said that although suspensory ligament damage is a serious injury that can affect the horse in the long term, with the right treatment there is a good chance of recovery. Above all, through targeted preventive measures you can reduce the strain on your horse and ensure its long-term health.












